Change Healthcare says it has notified approximately 100 million Americans that their personal, financial and healthcare records may have been stolen in a February 2024 ransomware attack that caused the largest ever known data breach of protected health information.

Image: Tamer Tuncay, Shutterstock.com.
A ransomware attack at Change Healthcare in the third week of February quickly spawned disruptions across the U.S. healthcare system that reverberated for months, thanks to the company’s central role in processing payments and prescriptions on behalf of thousands of organizations.
In April, Change estimated the breach would affect a “substantial proportion of people in America.” On Oct 22, the healthcare giant notified the U.S. Department of Health and Human Resources (HHS) that “approximately 100 million notices have been sent regarding this breach.”
A notification letter from Change Healthcare said the breach involved the theft of:
-Health Data: Medical record #s, doctors, diagnoses, medicines, test results, images, care and treatment;
-Billing Records: Records including payment cards, financial and banking records;
-Personal Data: Social Security number; driver’s license or state ID number;
-Insurance Data: Health plans/policies, insurance companies, member/group ID numbers, and Medicaid-Medicare-government payor ID numbers.
The HIPAA Journal reports that in the nine months ending on September 30, 2024, Change’s parent firm United Health Group had incurred $1.521 billion in direct breach response costs, and $2.457 billion in total cyberattack impacts.
Those costs include $22 million the company admitted to paying their extortionists — a ransomware group known as BlackCat and ALPHV — in exchange for a promise to destroy the stolen healthcare data.
That ransom payment went sideways when the affiliate who gave BlackCat access to Change’s network said the crime gang had cheated them out of their share of the ransom. The entire BlackCat ransomware operation shut down after that, absconding with all of the money still owed to affiliates who were hired to install their ransomware.
A few days after BlackCat imploded, the same stolen healthcare data was offered for sale by a competing ransomware affiliate group called RansomHub.
“Affected insurance providers can contact us to prevent leaking of their own data and [remove it] from the sale,” RansomHub’s victim shaming blog announced on April 16. “Change Health and United Health processing of sensitive data for all of these companies is just something unbelievable. For most US individuals out there doubting us, we probably have your personal data.”
It remains unclear if RansomHub ever sold the stolen healthcare data. The chief information security officer for a large academic healthcare system affected by the breach told KrebsOnSecurity they participated in a call with the FBI and were told a third party partner managed to recover at least four terabytes of data that was exfiltrated from Change by the cybercriminal group. The FBI declined to comment.
Change Healthcare’s breach notification letter offers recipients two years of credit monitoring and identity theft protection services from a company called IDX. In the section of the missive titled “Why did this happen?,” Change shared only that “a cybercriminal accessed our computer system without our permission.”
But in June 2024 testimony to the Senate Finance Committee, it emerged that the intruders had stolen or purchased credentials for a Citrix portal used for remote access, and that no multi-factor authentication was required for that account.
Last month, Sens. Mark Warner (D-Va.) and Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) introduced a bill that would require HHS to develop and enforce a set of tough minimum cybersecurity standards for healthcare providers, health plans, clearinghouses and businesses associates. The measure also would remove the existing cap on fines under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, which severely limits the financial penalties HHS can issue against providers.
According to the HIPAA Journal, the biggest penalty imposed to date for a HIPAA violation was the paltry $16 million fine against the insurer Anthem Inc., which suffered a data breach in 2015 affecting 78.8 million individuals. Anthem reported revenues of around $80 billion in 2015.
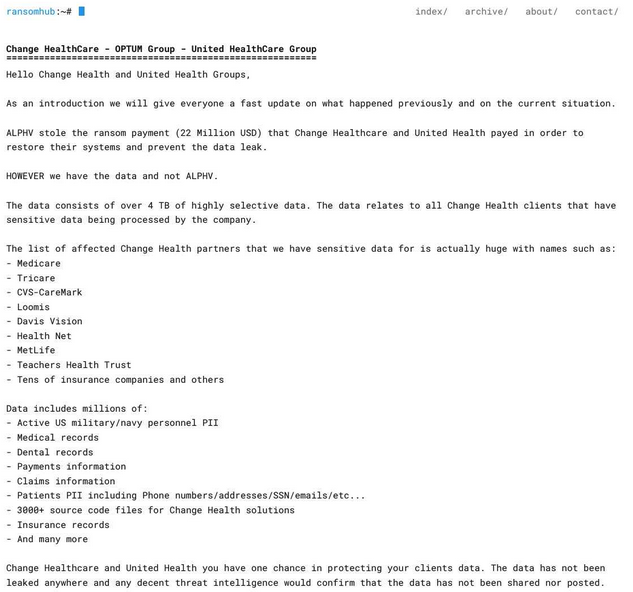
A post about the Change breach from RansomHub on April 8, 2024. Image: Darkbeast, ke-la.com.
There is little that victims of this breach can do about the compromise of their healthcare records. However, because the data exposed includes more than enough information for identity thieves to do their thing, it would be prudent to place a security freeze on your credit file and on that of your family members if you haven’t already.
The best mechanism for preventing identity thieves from creating new accounts in your name is to freeze your credit file with Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. This process is now free for all Americans, and simply blocks potential creditors from viewing your credit file. Parents and guardians can now also freeze the credit files for their children or dependents.
Since very few creditors are willing to grant new lines of credit without being able to determine how risky it is to do so, freezing your credit file with the Big Three is a great way to stymie all sorts of ID theft shenanigans. Having a freeze in place does nothing to prevent you from using existing lines of credit you may already have, such as credit cards, mortgage and bank accounts. When and if you ever do need to allow access to your credit file — such as when applying for a loan or new credit card — you will need to lift or temporarily thaw the freeze in advance with one or more of the bureaus.
All three bureaus allow users to place a freeze electronically after creating an account, but all of them try to steer consumers away from enacting a freeze. Instead, the bureaus are hoping consumers will opt for their confusingly named “credit lock” services, which accomplish the same result but allow the bureaus to continue selling access to your file to select partners.
If you haven’t done so in a while, now would be an excellent time to review your credit file for any mischief or errors. By law, everyone is entitled to one free credit report every 12 months from each of the three credit reporting agencies. But the Federal Trade Commission notes that the big three bureaus have permanently extended a program enacted in 2020 that lets you check your credit report at each of the agencies once a week for free.